What Are Hiccups?
Blue indicates link
If you have had them then you know the answer. They can be embarrassing and quite annoying. Here we will get into the technical issues and find out ways of getting rid of them if they happen to you.
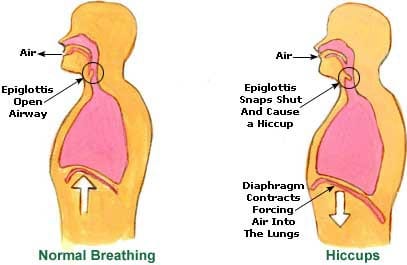
Hiccups are repetitive, uncontrollable contractions of the diaphragm muscle. Your diaphragm is the muscle just below your lungs. It marks the boundary between your chest and abdomen.
The diaphragm regulates breathing. When your diaphragm contracts, your lungs take in oxygen. When your diaphragm relaxes, your lungs release carbon dioxide.
The diaphragm contracting out of rhythm causes hiccups. Each spasm of the diaphragm makes the larynx and vocal cords close suddenly. This results in a sudden rush of air into the lungs. Your body reacts with a gasp or chirp, creating the sound characteristic of hiccups.
Hiccups start much lower in your body, though — in the diaphragm, the dome-shaped muscle between your lungs and stomach. Normally, the diaphragm pulls down when you inhale to let air into your lungs, and then relaxes when you exhale so air can flow back out of your lungs to exit your nose and mouth.
But if something irritates your diaphragm, it can spasm, forcing you to suddenly suck air into your throat, where it hits your voice box. That makes your vocal cords suddenly close, creating the distinct “hic!” sound.
Reasons For Having Hiccups
Hiccups can happen for a lot of reasons — some of them are physical, and some emotional. That’s because the actual irritation happens in the nerve connecting the brain to the diaphragm.
Some common causes of hiccups include:
- Eating too much or too quickly
- Feeling nervous or excited
- Stress
- A sudden change in temperature
- Swallowing air while sucking on candy or chewing gum.
Numerous causes of hiccups have been identified. However, there’s no definitive list of triggers. Hiccups often come and go for no apparent reason.
Other common causes of short-term hiccups include:
- overeating
- eating spicy food
- consuming alcohol
- drinking carbonated beverages, such as sodas
- consuming very hot or very cold foods
- a sudden change in air temperature
- excitement or emotional stress
- aerophagia (swallowing too much air)
Hiccups that last longer than 48 hours are categorized by the type of irritant that caused the episode.
The majority of persistent hiccups are caused by injury or irritation to either the vagus or phrenic nerve. The vagus and phrenic nerves control the movement of your diaphragm.
These nerves may be affected by:
- irritation of your eardrum, which may be caused by a foreign object.
- throat irritation or soreness
- a goiter (enlargement of the thyroid gland)
- gastroesophageal reflux (stomach acid backing up into the esophagus, the tube that moves food from the mouth to the stomach)
- an esophageal tumor or cyst
Other causes of hiccups may involve the central nervous system (CNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. If the CNS is damaged, your body may lose the ability to control hiccups.
CNS damage that may lead to persistent hiccups includes:
- stroke
- Multiple sclerosis (a chronic, degenerative nerve disease)
- tumors
- Meningitis and encephalitis (infections that can cause swelling in the brain)
- head trauma or brain injury
- Hydrocephalus (accumulation of fluid on the brain)
- neurosyphilis and other brain infections
Hiccups that last for longer periods can also be caused by:
- overuse of alcohol
- tobacco use
- An anesthesia reaction after surgery
- certain classes of drugs, including barbiturates, steroids, and tranquilizers
- diabetes
- an electrolyte imbalance
- kidney failure
- arteriovenous malformation (a condition in which arteries and veins are tangled in the brain)
- cancer and chemotherapy treatments
- Parkinson’s disease (a degenerative brain disease)
Sometimes, a medical procedure can accidentally cause you to develop long-term hiccups.
These procedures are used to treat or diagnose other conditions and include:
- use of catheters to access the heart muscle.
- placement of an esophageal stent to prop open the esophagus.
- Bronchoscopy (when an instrument is used to look inside your lungs)
- Tracheostomy (creation of a surgical opening in the neck to allow breathing around an airway obstruction)
What Causes Frequent Hiccups
Although most of us might get a bout of hiccups every so often, frequent hiccups are far more unusual and can sometimes be a sign of a more serious condition. Before we begin, however, we should get on the same page about what we mean by “frequent hiccups.” Generally, people don’t get a case of hiccups more than once a year and many people go through much of their adult lives without having even a single bout.
If, however, you are getting hiccups more than once a month, we might consider this a significant problem. You might also consider how long your bouts last. If your hiccups last for more than a few minutes or seem to be lasting longer and longer, you might want to try to get down to the cause of the problem.
Risk Factors for Hiccups
Hiccups can occur at any age. They can even occur while a fetus is still in the mother’s womb. However, there are several factors that can increase your likelihood of developing hiccups.
You may be more susceptible if you:
- are male.
- experience intense mental or emotional responses, ranging from anxiety to excitement.
- have received general anesthesia (you were put to sleep during surgery)
- had surgery, especially abdominal surgery.
Treating The Causes of Hiccups
Most hiccups aren’t an emergency or anything to worry about. However, a prolonged episode can be uncomfortable and disruptive to daily life.
Contact a doctor if you have hiccups that last longer than two days. They can determine the severity of your hiccups in relation to your overall health and other conditions.
There are numerous options for treating hiccups. Typically, a short-term case of hiccups will take care of itself. However, the discomfort may make waiting out hiccups unbearable if they last longer than a few minutes.
Although none of these have been proven to stop hiccups, the following potential treatments for hiccups can be tried at home:
- Breathe into a paper bag.
- Eat a teaspoon of granulated sugar.
- Hold your breath.
- Drink a glass of cold water.
- Pull on your tongue.
- Lift your uvula with a spoon. Your uvula is the fleshy piece of tissue that’s suspended above the back of your throat.
- Attempt to purposefully gasp or belch.
- Bring your knees to your chest and maintain this position.
- Try the Valsalva maneuver by shutting your mouth and nose and exhaling forcibly.
- Relax and breathe in a slow, controlled manner.
If you still have hiccups after 48 hours, talk to your doctor. Your doctor may attempt gastric lavage (stomach pumping) or carotid sinus massage (rubbing the main carotid artery in the neck).
If the cause of your hiccups is unclear, your doctor may recommend tests. These can help detect any underlying disease or condition.
The following tests may be useful in determining the cause of persistent or intractable hiccups:
- blood tests to identify signs of infection, diabetes, or kidney disease.
- liver function tests
- imaging of the diaphragm with a chest X-ray, CT scan, or MRI
- an echocardiogram to assess heart function.
- an endoscopy, which utilizes a thin, lighted tube with a camera on the end to investigate your esophagus, windpipe, stomach, and intestine.
- a bronchoscopy, which utilizes a thin, lighted tube with a camera on the end to examine your lungs and airways.
Treating any underlying causes of your hiccups will usually make them go away. If persistent hiccups have no obvious cause, there are several anti-hiccup medications that may be prescribed.
The more commonly used drugs include:
- chlorpromazine and haloperidol (antipsychotic medications)
- benzodiazepines (a class of tranquilizers)
- Benadryl (an antihistamine)
- Metoclopramide (a nausea drug)
- baclofen (a muscle relaxant)
- Nifedipine (a blood pressure medication)
- Seizure medications, such as gabapentin
There are also more invasive options, which can be used to end extreme cases of hiccups.
They include:
- nasogastric intubation (insertion of a tube through your nose into your stomach)
- an anesthetic injection to block your phrenic nerve.
- surgical implantation of a diaphragmatic pacemaker, a battery-powered device that stimulates your diaphragm and regulates breathing.
Possible complications of untreated hiccups
A long-term episode of hiccups can be uncomfortable and even harmful to your health. If left untreated, prolonged hiccups can disturb your sleeping and eating patterns, leading to:
- sleeplessness
- exhaustion
- malnutrition
- weight loss
- dehydration
How To Prevent Hiccups
There’s no proven method for preventing hiccups. However, if you experience hiccups frequently, you can try to reduce your exposure to known triggers.
The following may help reduce your susceptibility to hiccups:
- Don’t overeat.
- Avoid carbonated beverages.
- Protect yourself from sudden temperature changes.
- Don’t drink alcohol.
- Remain calm and try to avoid intense emotional or physical reactions.
Natural Ways to Stop Hiccups
- Hold your breath for 20 seconds. It will cut your hiccups.
- Breathe into a paper bag. Interestingly, it is really helpful to get rid of hiccups.
- Work on your breathing and try to breathe slowly. When you start to manage your breathing, hiccups will disappear.
- Apply pressure on your chest softly. Pay attention not to apply high pressure.
- Apply press-on your tongue. You need to apply a press in the middle of your tongue.
- Try to drink ice water or any other drinks.
- Suck on an ice cube.
- Suck a lemon.
- Press on your diaphragm. Try not to put much pressure on your body.
More On Getting Rid of Hiccups
Green Olive
Believe it or not, eating green olives when you have hiccups works like a charm every time. Green olives are pungent in taste and foods that are bitter, sour, or pungent are said to stop hiccups in a good natural way. Just pop an olive when you hic!!
Bend Down and Drink
This trick surely sounds weird but is very helpful in stopping hiccups in a natural way. Bend down from your waist and drink water from a cup placed on the floor via a straw. This posture is known to relax the diaphragm and stop hiccups. When persistent hiccups don’t stop this easy trick comes in handy.
Indulge In Eating Something Sweet
Overload the sensory nerves of your tongue with something sweet to do the trick. Try having a spoonful of sugar when you are troubled with hiccups. Some studies say that the phrenic nerves reset themselves following irritation of the esophagus and stop hiccups. However, there is no proof for this one. Try this folk remedy as a last resort if nothing else is working for you.
Sour-y Treats
As we mentioned earlier, foods that are sour can also work well to control hiccups. Taking a teaspoon of vinegar can stop hiccups in their tracks. Another option is to bite into a tangy lemon wedge, sucking its juice. The sour taste elicits the same effect as though someone is scaring you. Your body will react in a way to stop hiccups naturally.
Honey And Castor Oil
This ancient folk remedy for hiccups has its roots in Ayurveda. Mix 1 teaspoon of castor oil and honey each, dip your finger in the mixture, and lick your finger slowly. Repeat this trick 2-3 times. The honey and castor oil mix is known as an anti-hiccup militant that can help you regain your normal composure instantly.
Peanut Butter
Eating a spoonful of peanut butter or spreading it in your sandwiches and rolls has always been a healthy breakfast or snack option for many. But how many of us know that a spoonful of peanut butter when put in the mouth and held there for 10 seconds before swallowing stops hiccups?
You can also use almond butter or Nutella which has a sticky consistency to get rid of your hiccups.
Knees to Your Chest
Getting rid of hiccups is not easy all the time. However, you can try to relax the diaphragm by bringing your knees against your chest till the hiccups stop. It’s a simple posture therapy that helps you ease the condition.
Chocolate Remedy
This process of getting rid of hiccups isn’t as easy as it sounds. It’s not about eating a bar of your favorite chocolate. What you need to do is to eat powdered chocolate drink mix right from the spoon.
Chew Up Some Dill
Dill seeds are known to have many health benefits. Dill water is a known cure for digestion problems. These seeds can do another mind-blowing trick – hiccup treatment. Slowly chewing a spoonful of dill seeds is a traditional cure for hiccups. These seeds stimulate the vagus nerve and stop continuous hiccups.
What NOT To Do
- Assume attitudes and behaviors that can favor the onset of hiccups.
- Neglecting digestive complications.
- Promote the onset of anxiety by leading a stressful lifestyle.
- Do not treat the diseases (mentioned above) that favor the onset of hiccups.
- Eat solid, dry, or poorly chewable foods without accompanying the meal with a glass or two of water.
- Chew a little.
- Bring large pieces of food to your mouth at a time.
- Eat quickly.
- Eating standing up.
- Eating meals in stressful conditions or remaining anxious.
- Stay connected to multimedia or communication devices when eating.
- Hold back the belching.
- To get drunk.
There are no medical treatments or cures useful to prevent or stop hiccups, although therapeutic interventions for treating the primary diseases from which they derive could be considered decisive.
In case your hiccups continue, go to a doctor. Hiccups that last more than 48 hours long thought as dangerous. If you experience a situation of that duration, you need to consult a doctor or call an ambulance. Please do not take hiccups as something that just happens. There may be underlying medical issues that may cause regular hiccups.
Thank you for reading.
Michael
Comments are welcome.
I get hiccups any time I drink soda or carbonated beverages. That’s probably due to the air I swallow really quickly inside the can/bottle! This article helped explain why I experience that so often while proposing solutions to that very problem. This was very helpful. I think I usually just tried to belch the gas out but I might try the cold water method as well moving forward
Hi Quentin,
Thank you for your comments. I am sure the soda and carbonated beverages are one of the reasons for your hiccups. Drink slowly, and including water is a great idea.